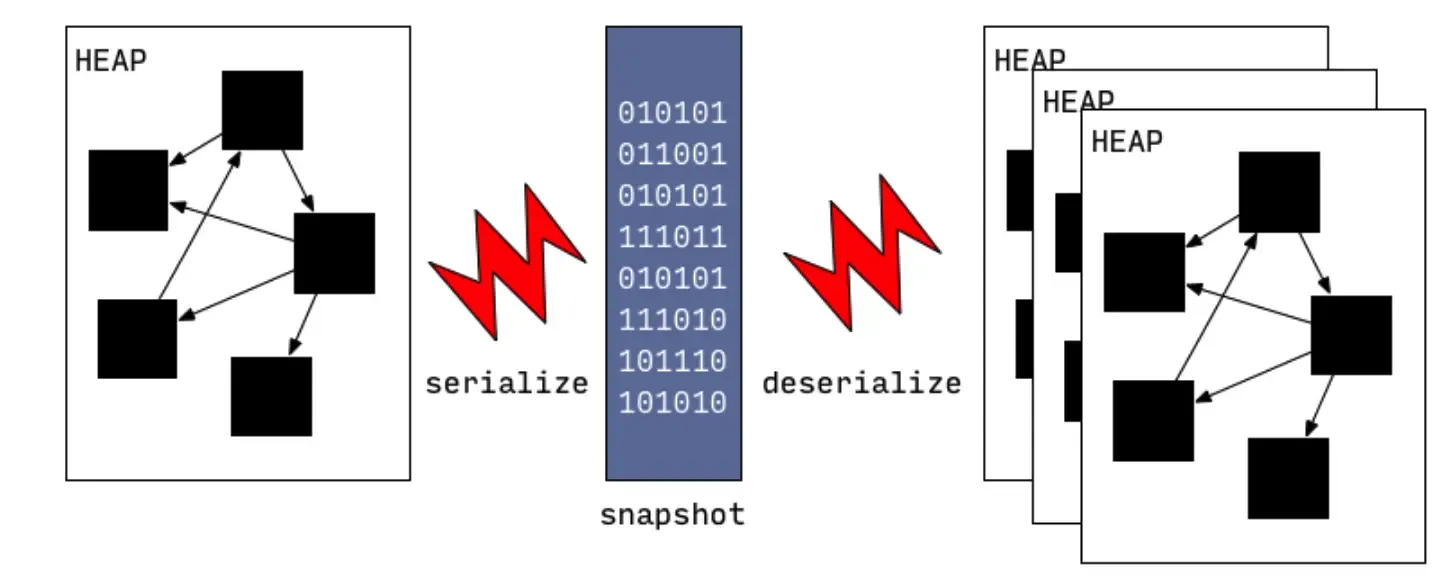
1.png
由于快照的序列化格式针对性的为读取速率做了设计,从快照读取也大大提高代码的加载速度(创建所需类信息、全局数据等,可以类比OC Runtime启动加载元类、类信息等)。最开始快照中是不包含机器代码的(即函数体内部的执行逻辑),后来随着AOT模式的开发这部分被加入到快照中了,这些后来者也就是前面说的Instructions。
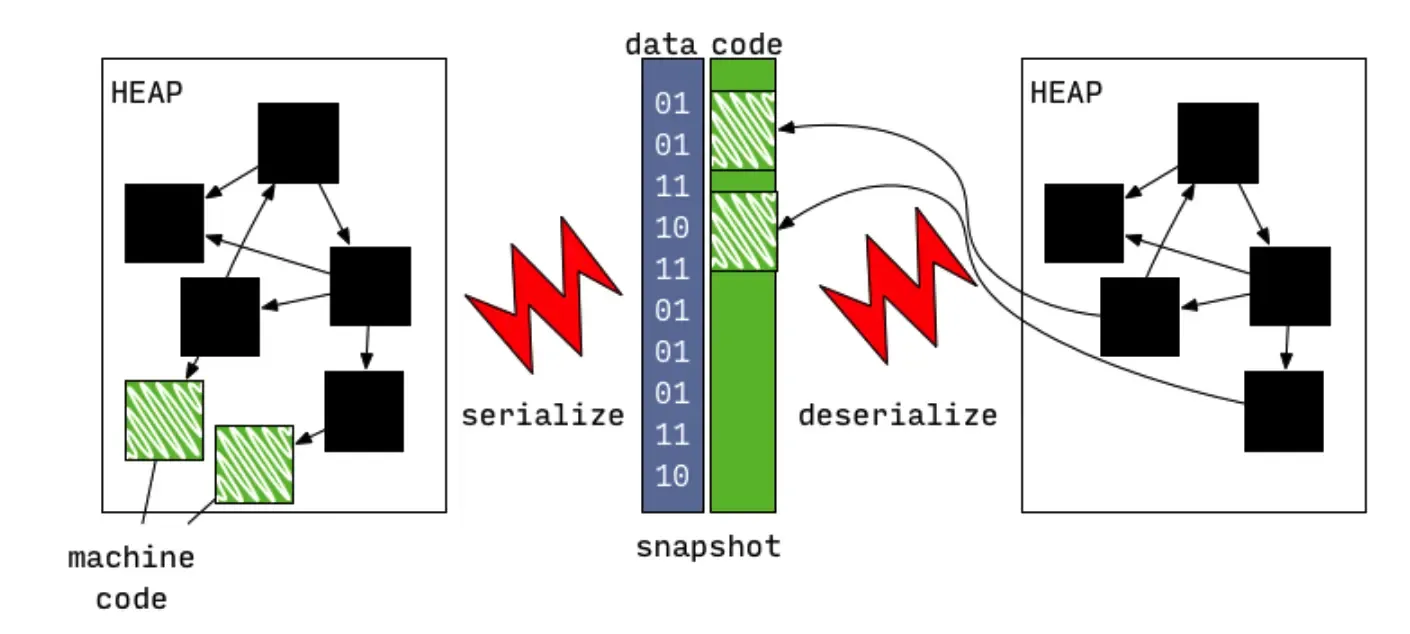
2.png
这里要补充的是,Instructions指的是可执行汇编指令,在.o文件中必须放在text段里,标记为可执行(否则iOS无法加载并执行它)。类信息、全局变量这些内容可以放在data端作为普通数据被加载。(字节的优化50%包体积也是基于此,有兴趣可以看一下文章:https://juejin.im/post/6844904014170030087)。
接着说DartVmSnapshot 与DartIsolateSnapshot。这就涉及Data虚拟机是如何运行业务代码。虚拟是Data代码运行的载体,VM中运行的逻辑都跑在一个抽象的叫做Isolate(隔离)的实体中。你可以把Isolate当做OC里一个带有Runloop的Thread看待(至于他们之间的关系又是一个令人头疼的面试题,这里不展开了)。简要来说Isolate中维护了堆栈变量,函数调用栈帧,用于GC、JIT等辅助任务的子线程等, 而这里的堆栈变量就是要被序列化到磁盘上的东西,即IsolateSnapshot。此外像dart预置的全局对象,比如null,true,false等等等是由VMIsolate管理的,这些东西需序列化后即VmSnapshot。
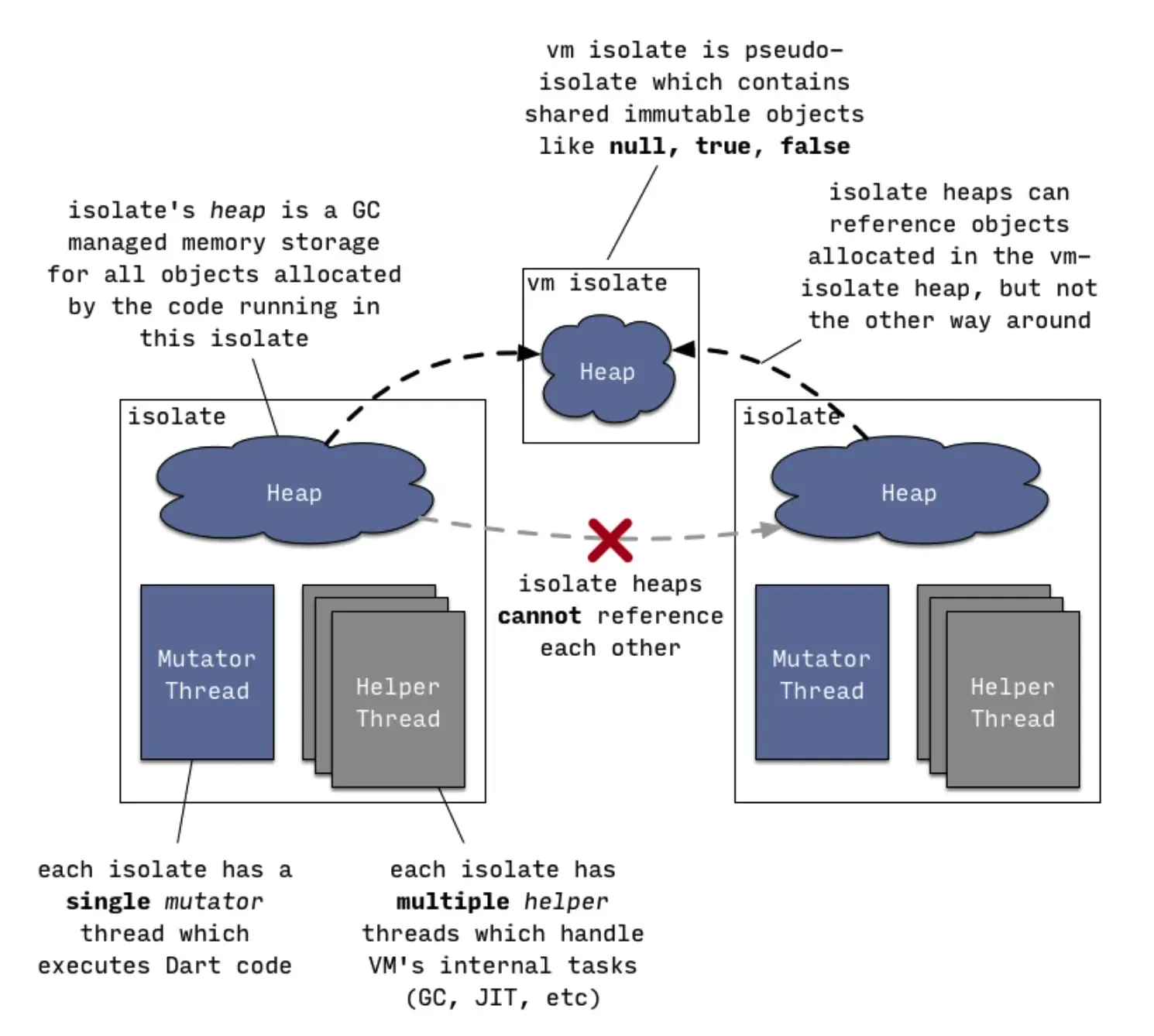
3.png
到这里大致了解Flutter APP产物中的结构。那如何读取他们呢?我们可以从clustered_snapshot.cc中的FullSnapshotReader:: 函数看起,看他是如何反序列化的。
void Deserializer::ReadIsolateSnapshot(ObjectStore* object_store) {
Array& refs = Array::Handle();
Prepare();
{
NoSafepointScope no_safepoint;
HeapLocker hl(thread(), heap_->old_space());
// N.B.: Skipping index 0 because ref 0 is illegal.
const Array& base_objects = Object::vm_isolate_snapshot_object_table();
for (intptr_t i = 1; i < base_objects.Length(); i++) {
AddBaseObject(base_objects.At(i));
}
Deserialize();
// Read roots.
RawObject** from = object_store->from();
RawObject** to = object_store->to_snapshot(kind_);
for (RawObject** p = from; p <= to; p++) {
*p = ReadRef();
}
#if defined(DEBUG)
int32_t section_marker = Read<int32_t>();
ASSERT(section_marker == kSectionMarker);
#endif
refs = refs_;
refs_ = NULL;
}
thread()->isolate()->class_table()->CopySizesFromClassObjects();
heap_->old_space()->EvaluateSnapshotLoad();
#if defined(DEBUG)
Isolate* isolate = thread()->isolate();
isolate->ValidateClassTable();
isolate->heap()->Verify();
#endif
for (intptr_t i = 0; i < num_clusters_; i++) {
clusters_[i]->PostLoad(refs, kind_, zone_);
}
// Setup native resolver for bootstrap impl.
Bootstrap::SetupNativeResolver();
}
要看懂这部分也是十分费力,另一个大神的分析文章可能会为我们带来很多启示:https://blog.tst.sh/reverse-engineering-flutter-apps-part-1/
我们要看如何读取RawObject对象
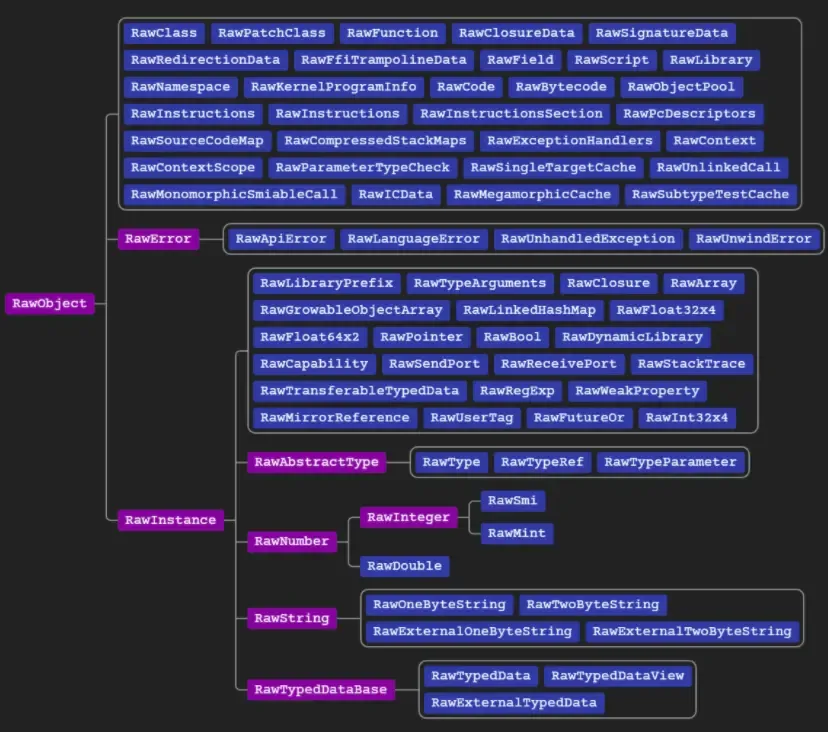
4.png
每个对象均以包含以下标记的uint32_t开头:
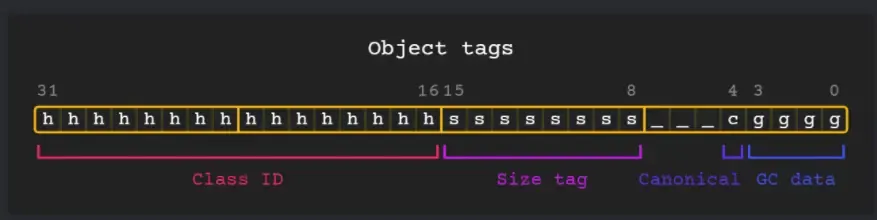
5.png
原则上我们自己可以写一个读取的程序进行分析,但是网上有一个使用Python写好的读取程序(只支持读取ELF格式文件,也就是只支持Android包产物的分析):https://github.com/hdw09/darter 基于这个读取工具提供的API我们可以写一个导出应用所有类定义的工具。
from darter.file import parse_elf_snapshot, parse_appjit_snapshot
from darter.asm.base import populate_native_references
import re
from collections import defaultdict
import os
import shutil
def get_funciont(fun_index, s, span=False):
spanStr = ''
if span:
spanStr = ' '
fun_str = '\n'+spanStr+'// 函数索引:' + '{0}'.format(fun_index)+'\n'
returnTypeStr = ''
if '_class' in s.refs[fun_index].x['result_type'].x.keys():
returnTypeStr = s.refs[fun_index].x['result_type'].x['_class'].x['name'].x['value']
elif 'name' in s.refs[fun_index].x['result_type'].x.keys():
returnTypeStr = str(s.refs[fun_index].x['result_type'])
else:
returnTypeStr = s.refs[fun_index].x['result_type'].x['value']
fun_str = fun_str+spanStr + returnTypeStr
fun_str = fun_str + ' ' + s.refs[fun_index].x['name'].x['value']+'('
parameterCount = 0
if type(s.refs[fun_index].x['parameter_types'].x['value']) != type(''):
for parameterName in s.refs[fun_index].x['parameter_names'].x['value']:
parType = ''
if '_class' in s.refs[fun_index].x['parameter_types'].x['value'][parameterCount].x.keys():
parType = s.refs[fun_index].x['parameter_types'].x['value'][parameterCount].x['_class'].x['name'].x['value']
else:
parType = s.refs[fun_index].x['parameter_types'].x['value'][parameterCount].x['value']
fun_str = fun_str + parType + ' '
fun_str = fun_str + parameterName.x['value'] + ', '
parameterCount = parameterCount + 1
fun_str = fun_str + ') \n'+spanStr+'{ \n'
for nrefsItem in s.refs[fun_index].x['code'].x['nrefs']:
fun_str = fun_str + spanStr + ' {0}'.format(nrefsItem) + '\n'
fun_str = fun_str + spanStr+'}'
return fun_str
def get_classDis(clas_index, s):
class_str = '\n// 类索引:' + '{0}'.format(clas_index)+' 使用s.refs[xxxx].x跟查\n'
superName = ''
if '_class' in s.refs[clas_index].x['super_type'].x.keys():
superName = s.refs[clas_index].x['super_type'].x['_class'].x['name'].x['value']
else:
superName = s.refs[clas_index].x['super_type'].x['value']
class_str = class_str + \
'class {0} : {1} {2}\n'.format(
s.refs[clas_index].x['name'].x['value'], superName, '{')
if type(s.refs[clas_index].x['functions'].x['value']) != type(''):
for fun in s.refs[clas_index].x['functions'].x['value']:
class_str = class_str+'\n'+get_funciont(fun.ref, s, True)
return class_str+'\n\n}'
def get_lob_class(lib, s):
all_class = ''
for item in lib.src:
if 'name' in item[0].x.keys():
all_class = all_class + get_classDis(item[0].ref, s) + '\n'
if '类索引' in all_class:
return all_class
else:
return '没有获得任何信息'
def show_lob_class(lib, s):
print(get_lob_class(lib, s))
def writeStringInPackageFile(packageFile, content):
packageFile = packageFile.replace('dart:', 'package:dart/')
filename = packageFile.replace('package:', 'out/')
filePath = filename[0:filename.rfind('/')]
content = '// {0} \n'.format(packageFile)+content
if os.path.exists(filePath) == False:
os.makedirs(filePath)
file = open(filename, 'w')
file.write(content)
file.close()
def getFiles(elfFile, filter):
s = parse_elf_snapshot(elfFile)
populate_native_references(s)
allLibrary = sorted(s.getrefs('Library'),
key=lambda x: x.x['url'].x['value'])
for tempLibrary in allLibrary:
name = tempLibrary.x['url'].x['value']
if filter in name:
print(name + '开始生成....')
writeStringInPackageFile(
name, get_lob_class(s.strings[name].src[1][0], s))
print(name + '生成成功')
# 开始执行
getFiles('samples/arm-app.so', '')
这个脚本最终会提取所有指定文件的源码,其中对友商app其中一个类的导出结果如下:
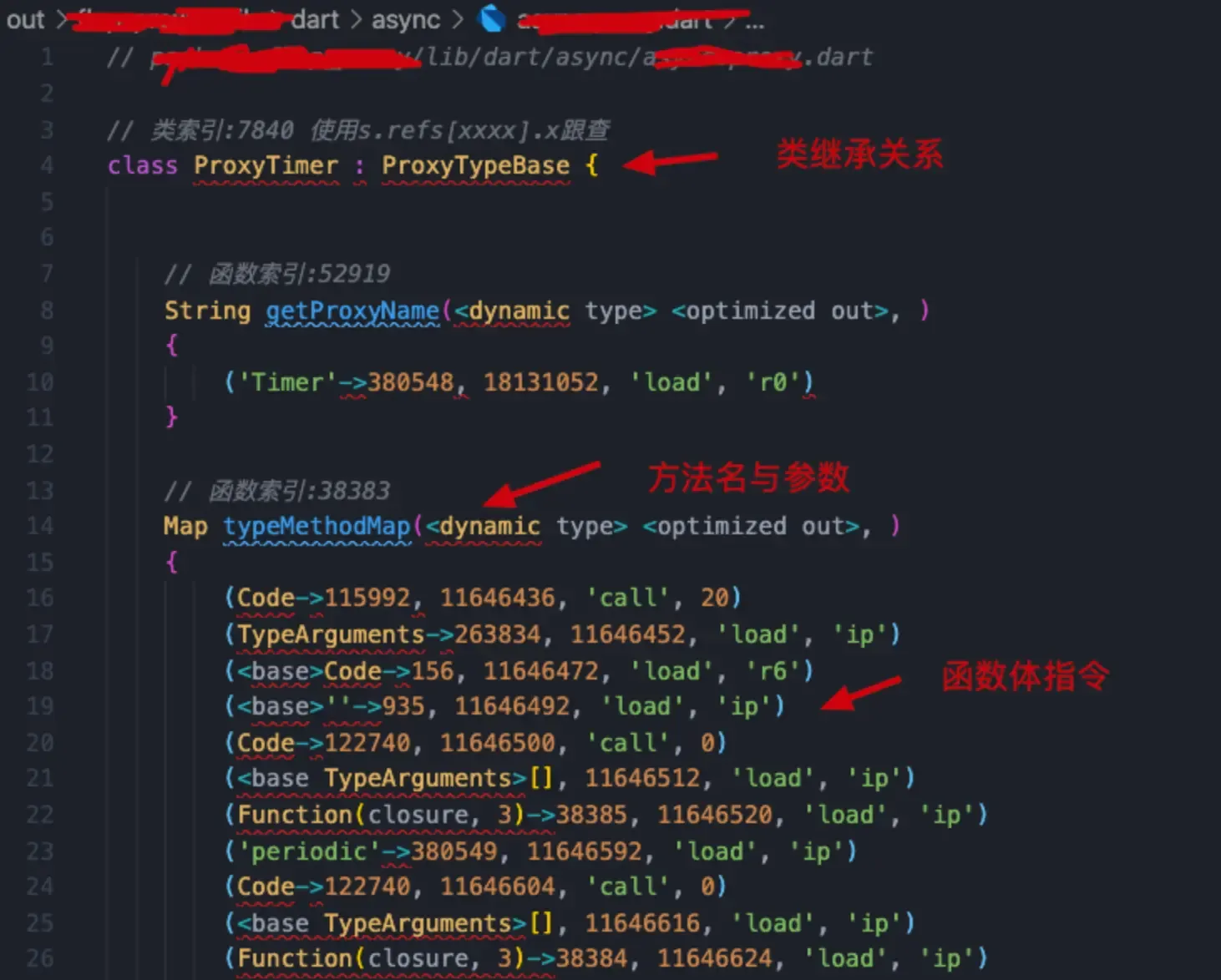
6.png
其中标注了类对象 与函数的索引,可以在控制台使用s.refs[xxxxx].x继续跟查。
文章均来自互联网如有不妥请联系作者删除QQ:314111741 地址:http://www.mqs.net/post/11433.html
添加新评论