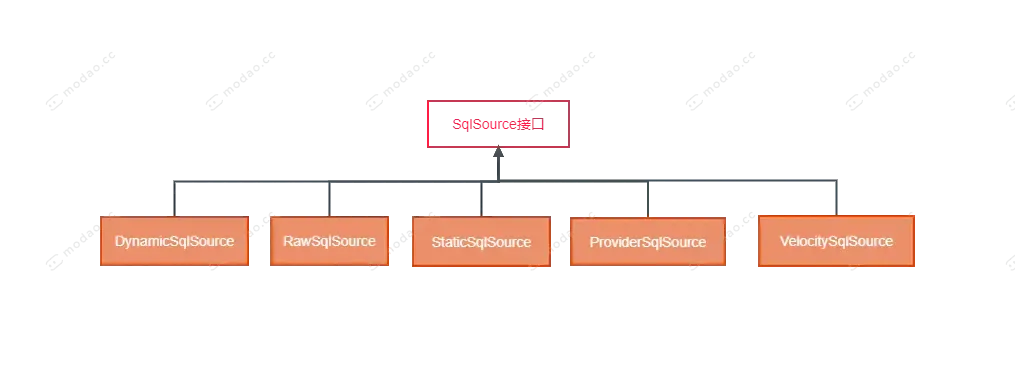
SqlSource接口.png
-
DynamicSqlSource
主要是封装动态SQL标签解析之后的SQL语句和带有${}的SQL语句
RawSqlSource
主要封装带有#{}的SQL语句
StaticSqlSource
是BoundSql中要存储SQL语句的一个载体,上面两个SqlSource的SQL语句,最终都会存储到该SqlSource实现类中
SqlSourceBuilder
主要完成了两方面的操作,一方面是解析Sql中的#{}占位符定义的属性,如jdbcType、javaType(使用较少),一方面是把#{}占位符替换成?占位符
ParameterMappingTokenHandler
SqlSourceBuilder的一个内部类,该类是解析#{}的核心。
GenericTokenParser
分词解析器
二、流程图
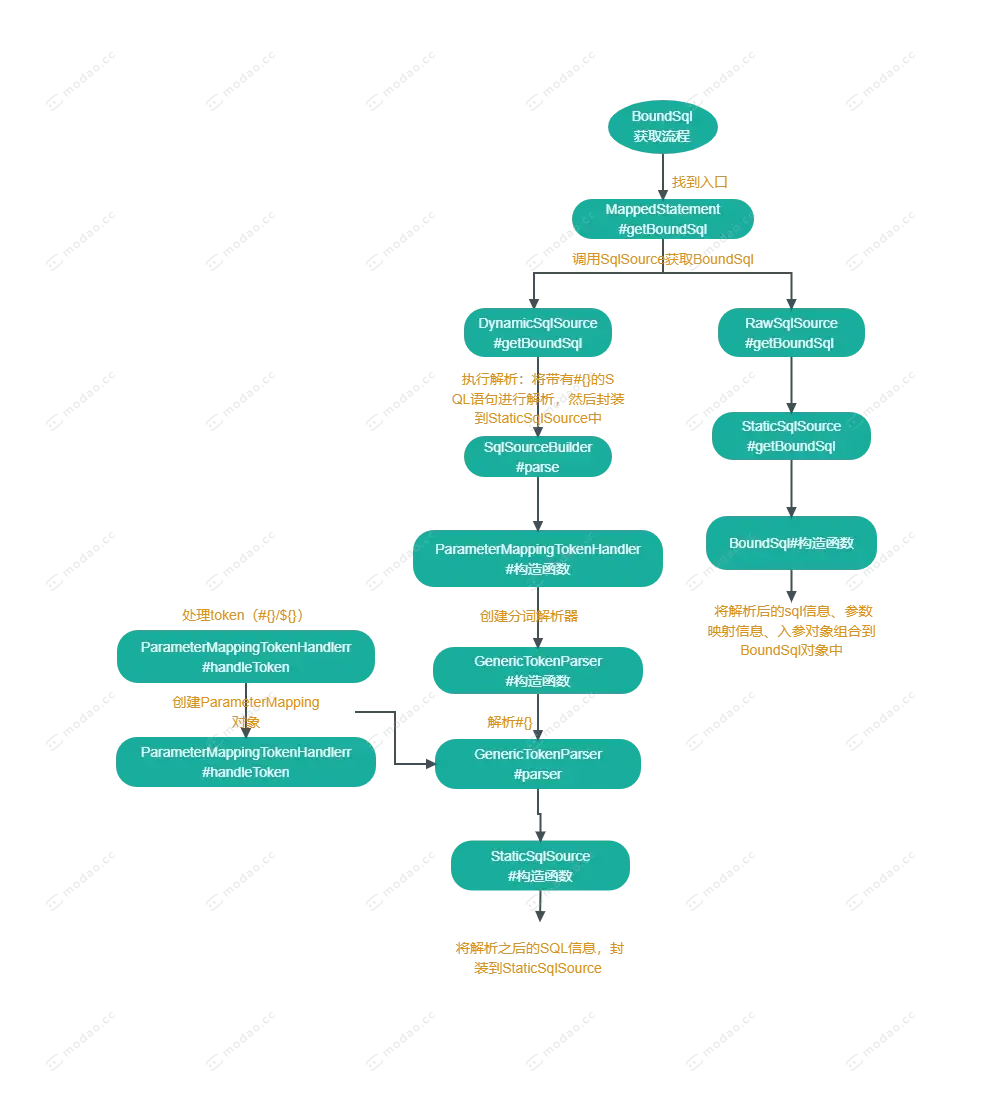
BoundSql获取流程.png
三、流程分析
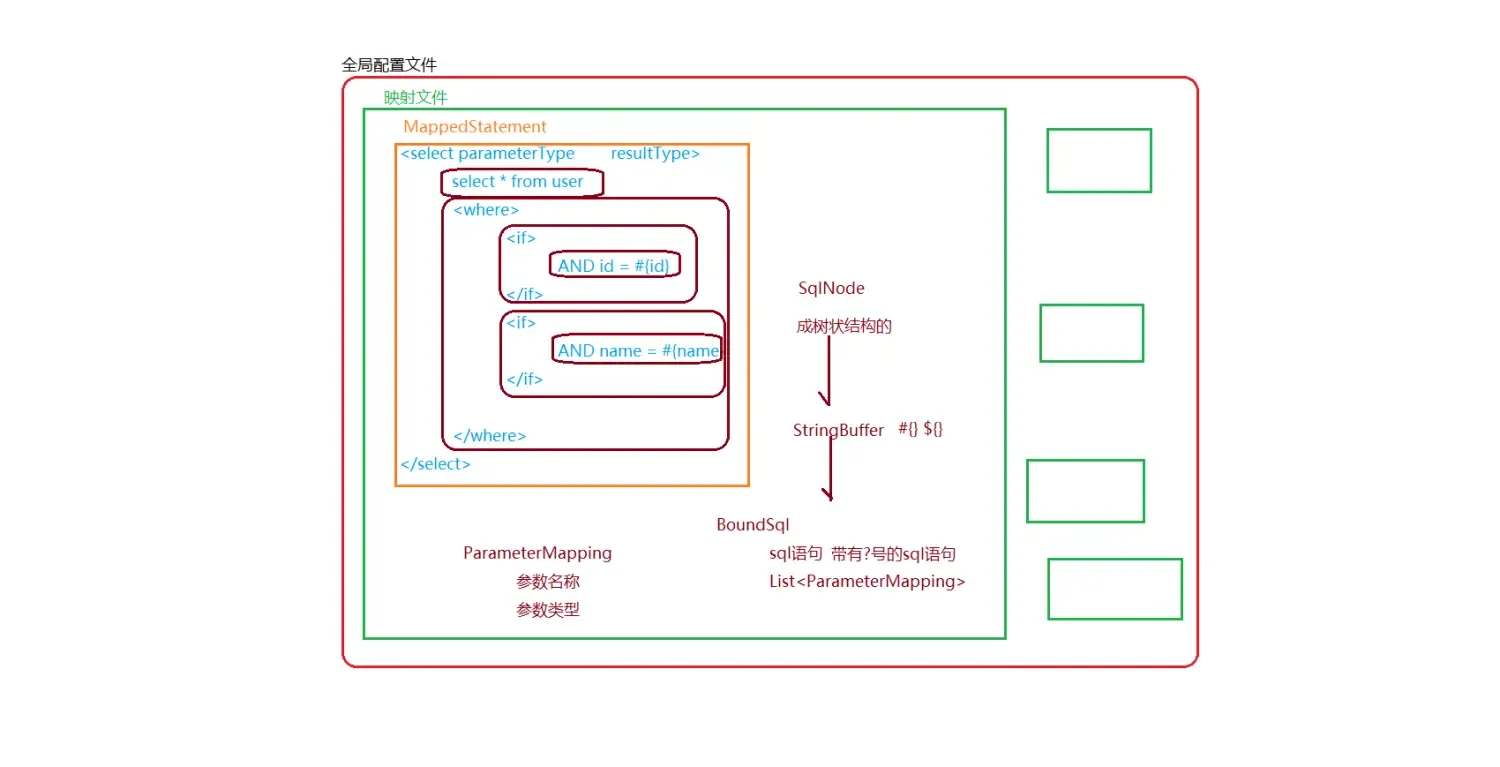
02.png
-
入口:MappedStatement#getBoundSql
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 调用SqlSource获取BoundSql
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings == null || parameterMappings.isEmpty()) {
boundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, boundSql.getSql(), parameterMap.getParameterMappings(), parameterObject);
}
// check for nested result maps in parameter mappings (issue #30)
for (ParameterMapping pm : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
String rmId = pm.getResultMapId();
if (rmId != null) {
ResultMap rm = configuration.getResultMap(rmId);
if (rm != null) {
hasNestedResultMaps |= rm.hasNestedResultMaps();
}
}
}
return boundSql;
}
-
DynamicSqlSource#getBoundSql
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);
// 此处会调用MixedSqlNode中包含的所有SqlNode的apply方法
// 此处会处理${},也会处理动态标签
// 最终将所有的SqlNode信息进行解析之后,追加到DynamicContext对象的StringBuilder对象中
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
// 创建SQL信息解析器
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
// 获取入参类型
Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();
// 执行解析:将带有#{}的SQL语句进行解析,然后封装到StaticSqlSource中
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
// 将解析后的SQL语句还有入参绑定到一起(封装到一个对象中,此时还没有将参数替换到SQL占位符?)
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : context.getBindings().entrySet()) {
boundSql.setAdditionalParameter(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
return boundSql;
}
-
流程图
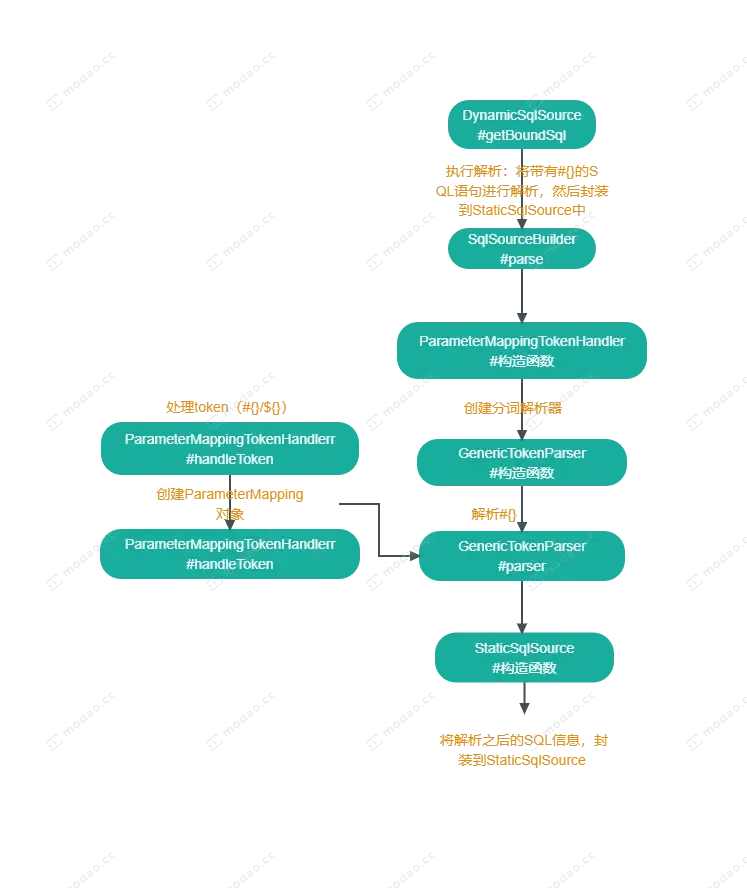
DynamicSqlSource#getBoundSql.png
-
1.SqlSourceBuilder#parse
执行解析:将带有#{}的SQL语句进行解析,然后封装到StaticSqlSource中
- 创建ParameterMappingTokenHandler
- 创建GenericTokenParser
- 然后解析originalSql
- 最后将解析之后的SQL信息,封装到StaticSqlSource对象中
public SqlSource parse(String originalSql, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
// 对#{}这样的字符串内容的解析处理类
ParameterMappingTokenHandler handler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler(configuration, parameterType,
additionalParameters);
// 创建分词解析器
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", handler);
// 解析#{}
String sql = parser.parse(originalSql);
// 将解析之后的SQL信息,封装到StaticSqlSource对象中
// SQL字符串是带有?号的字符串,?相关的参数信息,封装到ParameterMapping集合中
return new StaticSqlSource(configuration, sql, handler.getParameterMappings());
}
-
1.1 ParameterMappingTokenHandler#构造方法
public ParameterMappingTokenHandler(Configuration configuration, Class<?> parameterType,
Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
super(configuration);
this.parameterType = parameterType;
this.metaParameters = configuration.newMetaObject(additionalParameters);
}
-
1.2 GenericTokenParser#构造函数
创建分词解析器
public GenericTokenParser(String openToken, String closeToken, TokenHandler handler) {
this.openToken = openToken;
this.closeToken = closeToken;
this.handler = handler;
}
-
1.3 GenericTokenParser#parse
解析#{}
/**
* 解析${}和#{}
* @param text
* @return
*/
public String parse(String text) {
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
// search open token
int start = text.indexOf(openToken, 0);
if (start == -1) {
return text;
}
char[] src = text.toCharArray();
int offset = 0;
final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder expression = null;
while (start > -1) {
if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') {
// this open token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken);
offset = start + openToken.length();
} else {
// found open token. let's search close token.
if (expression == null) {
expression = new StringBuilder();
} else {
expression.setLength(0);
}
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset);
offset = start + openToken.length();
int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
while (end > -1) {
if (end > offset && src[end - 1] == '\\') {
// this close token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset - 1).append(closeToken);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
} else {
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
break;
}
}
if (end == -1) {
// close token was not found.
builder.append(src, start, src.length - start);
offset = src.length;
} else {
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));
offset = end + closeToken.length();
}
}
start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
}
if (offset < src.length) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
return builder.toString();
}
-
1.3.1 ParameterMappingTokenHandlerr#handleToken
处理token(#{}/${})
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
// 此处的作用就是对`#{}`节点中的key值保存映射,比如javaType/jdbcType/mode等信息
parameterMappings.add(buildParameterMapping(content));
// 将`#{}`替换为?,即一般包装成`select * form test where name=? and age=?`预表达式语句
return "?";
}
-
1.3.1.1 ParameterMappingTokenHandlerr#handleToken
创建ParameterMapping对象
private ParameterMapping buildParameterMapping(String content) {
Map<String, String> propertiesMap = parseParameterMapping(content);
String property = propertiesMap.get("property");
Class<?> propertyType;
if (metaParameters.hasGetter(property)) { // issue #448 get type from additional params
propertyType = metaParameters.getGetterType(property);
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterType)) {
propertyType = parameterType;
} else if (JdbcType.CURSOR.name().equals(propertiesMap.get("jdbcType"))) {
propertyType = java.sql.ResultSet.class;
} else if (property == null || Map.class.isAssignableFrom(parameterType)) {
propertyType = Object.class;
} else {
MetaClass metaClass = MetaClass.forClass(parameterType, configuration.getReflectorFactory());
if (metaClass.hasGetter(property)) {
propertyType = metaClass.getGetterType(property);
} else {
propertyType = Object.class;
}
}
ParameterMapping.Builder builder = new ParameterMapping.Builder(configuration, property, propertyType);
Class<?> javaType = propertyType;
String typeHandlerAlias = null;
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : propertiesMap.entrySet()) {
String name = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
if ("javaType".equals(name)) {
javaType = resolveClass(value);
builder.javaType(javaType);
} else if ("jdbcType".equals(name)) {
builder.jdbcType(resolveJdbcType(value));
} else if ("mode".equals(name)) {
builder.mode(resolveParameterMode(value));
} else if ("numericScale".equals(name)) {
builder.numericScale(Integer.valueOf(value));
} else if ("resultMap".equals(name)) {
builder.resultMapId(value);
} else if ("typeHandler".equals(name)) {
typeHandlerAlias = value;
} else if ("jdbcTypeName".equals(name)) {
builder.jdbcTypeName(value);
} else if ("property".equals(name)) {
// Do Nothing
} else if ("expression".equals(name)) {
throw new BuilderException("Expression based parameters are not supported yet");
} else {
throw new BuilderException("An invalid property '" + name + "' was found in mapping #{" + content
+ "}. Valid properties are " + parameterProperties);
}
}
if (typeHandlerAlias != null) {
builder.typeHandler(resolveTypeHandler(javaType, typeHandlerAlias));
}
return builder.build();
}
-
1.4 StaticSqlSource#构造函数
将解析之后的SQL信息,封装到StaticSqlSource对象中,SQL字符串是带有?号的字符串,?相关的参数信息,封装到ParameterMapping集合中
public StaticSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings) {
this.sql = sql;
this.parameterMappings = parameterMappings;
this.configuration = configuration;
}
-
RawSqlSource#getBoundSql
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
return sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
-
StaticSqlSource#getBoundSql
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
return new BoundSql(configuration, sql, parameterMappings, parameterObject);
}
-
BoundSql#构造函数
将解析后的sql信息、参数映射信息、入参对象组合到BoundSql对象中
public BoundSql(Configuration configuration, String sql, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings, Object parameterObject) {
this.sql = sql;
this.parameterMappings = parameterMappings;
this.parameterObject = parameterObject;
this.additionalParameters = new HashMap<>();
this.metaParameters = configuration.newMetaObject(additionalParameters);
}
文章均来自互联网如有不妥请联系作者删除QQ:314111741 地址:http://www.mqs.net/post/15236.html

添加新评论